2023. 11. 21. 14:54ㆍML&DL/CV
[분리수거 Multi-Class Classification]
* glass / paper / cardboard/ plastic / metal /trash
- 6개의 클래스로 Multi-Class 분류 해보기
- trash 는 나머지 5개의 클래스에 들어가지 않는 기타 클래스를 의미함
├─garbage
│ └─raw
│ ├─glass : 501 files
│ ├─paper : 594 files
│ ├─cardboard : 403 files
│ ├─plastic : 482 files
│ ├─metal : 410 files
│ └─trash : 137 files* 데이터셋
- 총 2527 장의 데이터
https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/asdasdasasdas/garbage-classification
Garbage Classification
6 classes: cardboard, glass, metal , paper, plastic and trash.
www.kaggle.com
* 개발 환경
- colab
💻 실습
* 데이터 불러오기
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from PIL import Image
dir_main = "../../data/garbage/"
phase = "raw"
classes = ['cardboard', 'glass', 'metal', 'paper', 'plastic', 'trash']
for i in range(5):
image_paths = [f"{os.path.join(dir_main, phase, cls, cls+f'{i+1}.jpg')}" for cls in classes]
images = [Image.open(image_path) for image_path in image_paths]
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=len(classes), figsize=(15,2))
for idx, (cls, img) in enumerate(zip(classes, images)):
axes[idx].set_title(f"{cls}{str(i+1)}.jpg")
axes[idx].imshow(img)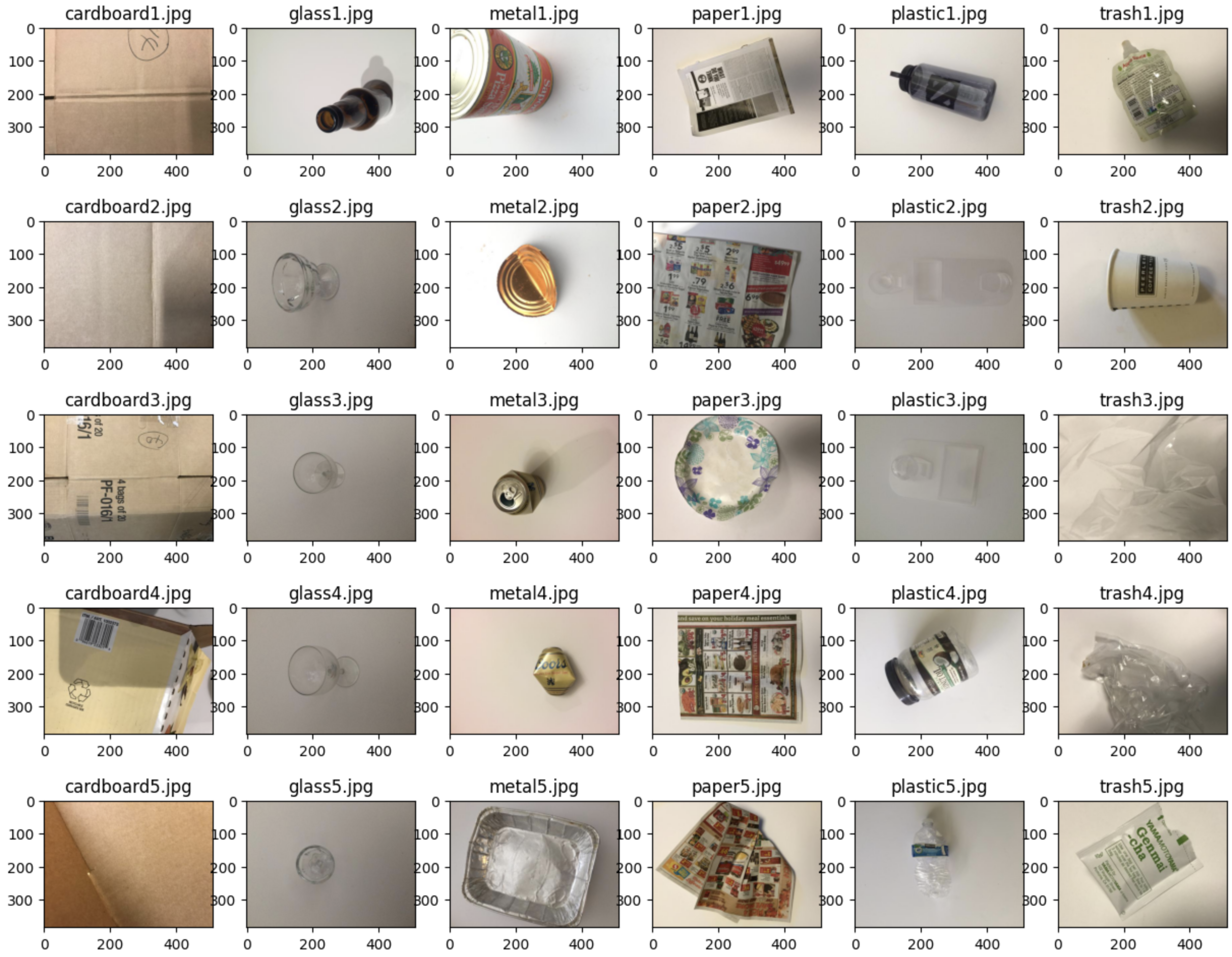
* 데이터 train/val/test 분할
- train 과 test 를 7:3으로 나눔
- 나눈 test 데이터를 다시 test:val= 5:5 로 나눔
import os
import numpy as np
from glob import glob
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
np.random.seed(724)
dir_main = "../../data/garbage/"
dir_data_original = os.path.join(dir_main, 'raw')
classes = glob(f"{dir_data_original}/*")
class_info = {idx : os.path.basename(cls) for idx, cls in enumerate(classes)}
img_files = glob(f"{dir_data_original}/*/*.jpg")
dataset = np.array([[img_file, img_file.split("/")[-2]] for img_file in img_files])
x = dataset[:,0]
y = dataset[:,1]
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, train_size=0.7, random_state=724)
x_val, x_test, y_val, y_test = train_test_split(x_test, y_test, train_size=0.5, random_state=724)
* 학습에 사용할 디렉토리를 만들어주고 분할한 train/test/val 데이터를 복사
def create_symlink(x_target, name='train'):
for x in x_target:
src = os.path.abspath(x)
dst = src.replace("Garbage", name)
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(dst), exist_ok=True)
if not os.path.exists(dst):
os.symlink(src, dst)
create_symlink(x_train, "train")
create_symlink(x_test, "test")
create_symlink(x_val, "val")
def get_numbers(ys, cls=None):
cls_cnt = {}
for y in ys:
if y not in cls_cnt.keys():
cls_cnt[y]=0
cls_cnt[y]+=1
if cls is None:
return cls_cnt
return cls_cnt[cls]
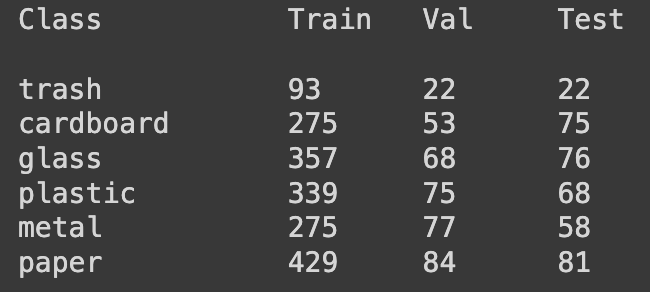
print(f"Class\t\tTrain\tVal\tTest\n")
for cls in class_info.values():
print(f"{cls:10}\t{get_numbers(y_train, cls)}\t{get_numbers(y_val, cls)}\t{get_numbers(y_test, cls)}")
* 데이터 로더 및 전처리 함수 생성
import torch
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from glob import glob
class GarbageDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, dir_dataset, tr):
self.dir_dataset = os.path.abspath(dir_dataset)
self.filelist = glob(self.dir_dataset + '/*.jpg')
assert len(self.filelist)!=0, f"{self.dir_dataset + '/*.jpg'} is empty"
self.classes = ['cardboard', 'glass', 'metal', 'paper', 'plastic', 'trash']
self.tr = tr
def get_image(self, filename):
img = Image.open(filename)
img = self.tr(img)
return img
def get_label(self, filename):
label = np.array([0] * len(self.classes))
cls = filename.split('/')[-2]
label[self.classes.index(cls)] = 1
return torch.from_numpy(label).type(torch.FloatTensor)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
filename = self.filelist[idx]
img = self.get_image(filename)
label = self.get_label(filename)
return img, label
def __len__(self):
return len(self.filelist)GarbageDataset 클래스
* 이미지 데이터 로드 & 전처리 클래스
- __init__ : 클래스 라벨과 이미지 파일의 리스트 설정
- get_image : 이미지 파일 읽기
- get_label : 이미지 파일에서 클래스 라벨 추출 후 원핫 인코딩 수행
- __getitem__ : 인덱스에 해당하는 이미지와 라벨 반환
- __len__ : 데이터셋 총 길이 반환
* 이미지 전처리
- 리사이즈, 이미지 크롭, 뒤집기, 회전, 정규화 과정을 train, val, test 데이터셋에 실행
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torchvision.transforms as T
# print(model.default_cfg['mean']) # 'mean': (0.485, 0.456, 0.406)
# print(model.default_cfg['std']) # 'std': (0.229, 0.224, 0.225)
normalize = T.Normalize(
mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]
)
'''
Resize: 이미지 크기를 조정합니다.
CenterCrop: 이미지의 중앙 부분을 잘라냅니다.
RandomCrop: 이미지에서 무작위로 부분을 잘라냅니다.
RandomHorizontalFlip: 이미지를 수평 방향으로 무작위로 뒤집습니다.
RandomRotation: 이미지를 주어진 각도 범위 내에서 무작위로 회전시킵니다.
ToTensor: 이미지 데이터를 PyTorch 텐서로 변환합니다.
Normalize: 텐서를 주어진 평균 및 표준 편차 값으로 정규화합니다.
'''
train_tr = T.Compose([
T.Resize((256, 256)),
T.RandomCrop(224),
T.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
T.ToTensor(),
normalize
])
test_tr = T.Compose([
T.Resize((224, 224)),
T.ToTensor(),
normalize
])
test_dir='/content/drive/MyDrive/test_classification'
tr_dir= '/content/drive/MyDrive/train_classification'
val_dir= '/content/drive/MyDrive/val_classification'
train_ds = GarbageDataset(os.path.join(tr_dir, "train"), train_tr)
val_ds = GarbageDataset(os.path.join(val_dir, "val"), test_tr)
test_ds = GarbageDataset(os.path.join(test_dir, "test"), test_tr)
train_dl = DataLoader(train_ds, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, batch_size=64)
val_dl = DataLoader(val_ds, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, batch_size=64)
test_dl = DataLoader(test_ds, shuffle=True, num_workers=0, batch_size=64)
* 모델
- EfficientNet : 라이브러리 timm에서 제공하는 pre-trained 모델
* 모델 불러오기
!pip install timm- efficitentnet 모델 리스트 출력
import timm
print(f"The number of pretrained models : {len(timm.list_models('*', pretrained=True))}")
timm.list_models('efficientnet*', pretrained=True)The number of pretrained models : 1289
['efficientnet_b0.ra_in1k',
'efficientnet_b1.ft_in1k',
'efficientnet_b1_pruned.in1k',
'efficientnet_b2.ra_in1k',
'efficientnet_b2_pruned.in1k',
'efficientnet_b3.ra2_in1k',
'efficientnet_b3_pruned.in1k',
'efficientnet_b4.ra2_in1k',
'efficientnet_b5.sw_in12k',
'efficientnet_b5.sw_in12k_ft_in1k',
'efficientnet_el.ra_in1k',
'efficientnet_el_pruned.in1k',
'efficientnet_em.ra2_in1k',
'efficientnet_es.ra_in1k',
'efficientnet_es_pruned.in1k',
'efficientnet_lite0.ra_in1k',
'efficientnetv2_rw_m.agc_in1k',
'efficientnetv2_rw_s.ra2_in1k',
'efficientnetv2_rw_t.ra2_in1k']
- 그 중 efficientnet_b0 사용
model = timm.create_model('efficientnet_b0', pretrained=True)
model.default_cfg
* 모델 구조 확인
# check output dimension
print(model.global_pool)
print(model.get_classifier())SelectAdaptivePool2d(pool_type=avg, flatten=Flatten(start_dim=1, end_dim=-1))
Linear(in_features=1280, out_features=1000, bias=True)
* 풀링 타입 확인
- 각 풀링 타입에 대한 크기 출력
import torch
pool_types = ['avg', 'max', 'avgmax', 'catavgmax', '']
for pool in pool_types:
model = timm.create_model('efficientnet_b0', pretrained=True, num_classes=0, global_pool=pool)
model.eval()
feature_output = model(torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224))
print(feature_output.shape)
* 풀링 - max pooling 선택
model.reset_classifier(len(classes), 'max')
print(model.global_pool)
print(model.get_classifier())* 특성 맵 크기 확인
num_in_features = model.get_classifier().in_features
num_in_features
* 모델 구조 정의 - 불러온 efficitentnet 모델에 대한 전이 학습
from torch import nn
model.fc = nn.Sequential(
nn.BatchNorm1d(num_in_features),
nn.Linear(in_features=num_in_features, out_features=512, bias=False),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.BatchNorm1d(512),
nn.Dropout(0.4),
nn.Linear(in_features=512, out_features=6, bias=False)
)model = timm.create_model('efficientnet_b0', pretrained=True, num_classes=len(classes), global_pool='avg')
* (1,3,224,224)
model.eval()
model(torch.randn(1, 3, 224, 224)).shape
- 1 : 배치 사이즈, 한번에 한 장씩 전달
- 3 : 컬러 이미지(RGB), 흑백일 경우 1
- 224,224: 이미지 전처리 과정에서 224,224로 리사이즈 했으므로 적용
import timm
import torch.nn.functional as F
class EfficientNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.model = timm.create_model('efficientnet_b0', pretrained=True, num_classes=len(classes), global_pool='avg')
def forward(self, x):
return torch.sigmoid(self.model(x))
model = EfficientNet()
#to_device(model, device)
* 모델 학습
* 학습 모델 평가 함수 정의
- 에포크별로 pickle 파일에 저장
- accuracy, loss 값 출력
import pickle
import os
class TrainHelper():
def __init__(self, save_path='./ckpt/history.pickle', history=[]):
self.history = history
self.save_path = save_path
os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(save_path), exist_ok=True)
def accuracy(self, outputs, labels):
pred = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
gt = torch.max(labels, dim=1)[1]
return torch.tensor(torch.sum(pred == gt).item() / len(pred))
@torch.no_grad()
def validation(self, batch):
images, labels = batch
out = model(images)
acc = self.accuracy(out, labels)
loss = F.cross_entropy(out, labels)
return {'val_loss': loss.detach(), 'val_acc': acc}
@torch.no_grad()
def evaluation(self, model, data_loader):
model.eval()
outputs = [self.validation(batch) for batch in data_loader]
batch_losses = [x['val_loss'] for x in outputs]
epoch_loss = torch.stack(batch_losses).mean()
batch_accs = [x['val_acc'] for x in outputs]
epoch_acc = torch.stack(batch_accs).mean()
return {'val_loss': round(epoch_loss.item(), 5), 'val_acc': round(epoch_acc.item(), 5)}
def logging(self, epoch, result):
print("Epoch {}: train_loss: {:.4f}, val_loss: {:.4f}, val_acc: {:.4f}".format(
epoch, result['train_loss'], result['val_loss'], result['val_acc']))
self.history.append(result)
with open(self.save_path, 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(self.history, f)
train_helper = TrainHelper()
* 학습
from tqdm import tqdm
epochs = 20
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), 5.5e-5)
val_acc_best = 0
save_model_path = "./ckpt/"
os.makedirs(save_model_path, exist_ok=True)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# Training Phase
model.train()
train_losses = []
for batch in tqdm(train_dl):
inputs, targets = batch
outputs = model(inputs)
loss = F.cross_entropy(outputs, targets)
train_losses.append(loss)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
# Validation phase
result = train_helper.evaluation(model, val_dl)
result['train_loss'] = torch.stack(train_losses).mean().item()
# Save the best model
if result['val_acc'] >= val_acc_best:
val_acc_best = result['val_acc']
if 'save_model_name' in locals() and os.path.exists(save_model_name):
os.remove(save_model_name)
save_model_name = os.path.join(save_model_path, f"best_ep_{epoch}_{val_acc_best}.pt")
torch.save(model.state_dict(), save_model_name)
print(f"Saved PyTorch Model State to {save_model_name}")
train_helper.logging(epoch, result)
# Save the last model
save_model_name = os.path.join(save_model_path, f"last_ep_{epoch}_{val_acc_best}.pt")
torch.save(model.state_dict(), save_model_name)
* 학습 현황 시각화
- train_loss / val_loss
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
train_loss = [history['train_loss'] for history in train_helper.history]
val_loss = [history['val_loss'] for history in train_helper.history]
plt.plot(train_loss, label='train loss')
plt.plot(val_loss, label='Validation loss')
plt.grid()
plt.legend(frameon=False)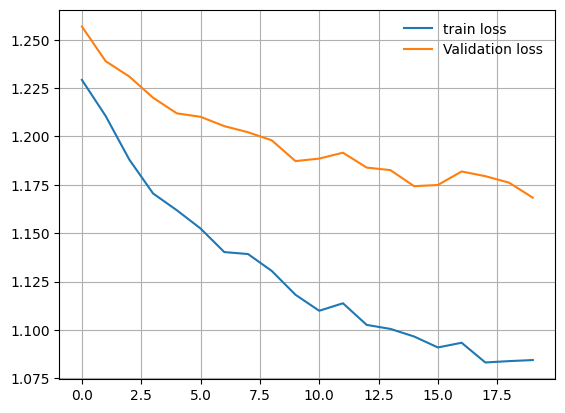
- accuracy
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
val_acc = [history['val_acc'] for history in train_helper.history]
plt.plot(val_acc, label='Accuracy')
plt.grid()
plt.legend(frameon=False)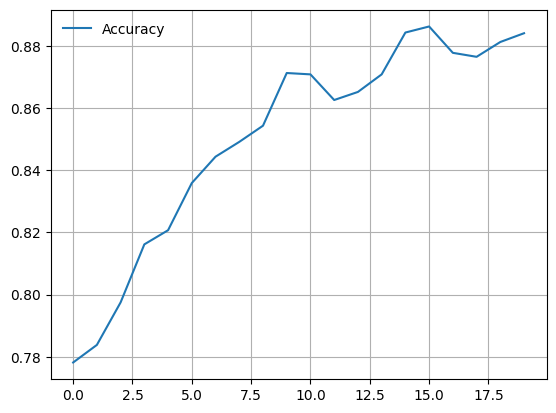
* 학습 결과
from sklearn import metrics
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
model.eval()
y_pred = []
y_true = []
for batch in tqdm(test_dl):
inputs, targets = batch
outputs = model(inputs)
y_pred.extend(torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1].numpy())
y_true.extend(torch.max(targets, dim=1)[1].numpy())
performance = metrics.classification_report(y_true, y_pred, digits=3)
confusion_matrix = metrics.confusion_matrix(y_true, y_pred)
classes = test_ds.classes
disp = metrics.ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix = confusion_matrix, display_labels = list(range(len(classes))))
print(f"Classes : {classes}")
print(f"Performance \n{performance}")
disp.plot()
fig = disp.ax_.get_figure()
fig.set_figwidth(len(classes))
fig.set_figheight(len(classes))
plt.savefig("confusion_matrix.jpg")
plt.show()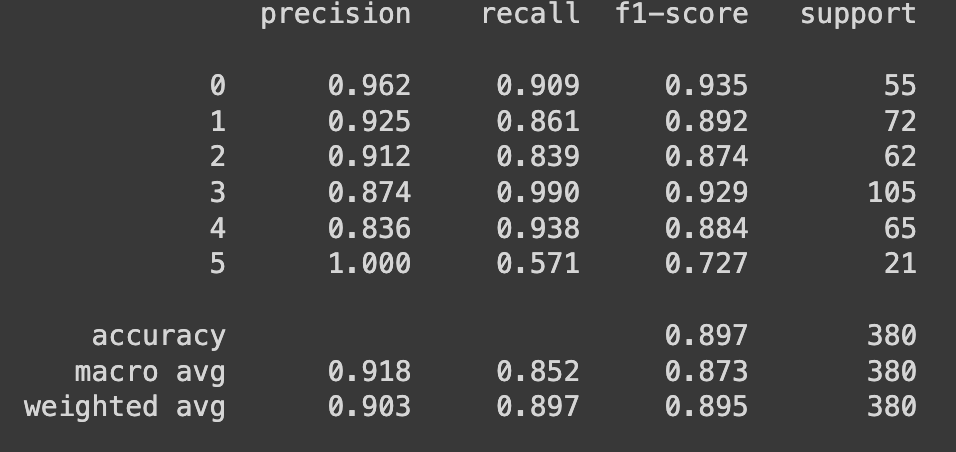
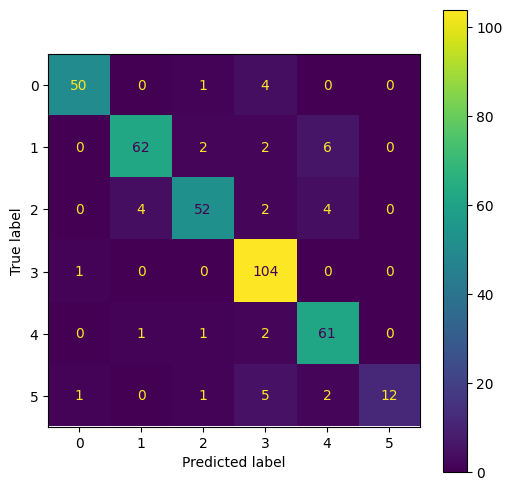
cardboard : 0, glass : 1, metal : 2, paper : 3 , plastic: 4, trash: 5
* 혼동 행렬
ex) 정확도가 가장 낮은 플라스틱(4) 클래스는 전체 73 개 중 61개 정답, 12개 오답
=> 오답 중 6개가 유리로 예측했다. 플라스틱과 유리가 좀 헷갈리나보다
* 테스트
- 오답 케이스 살펴보기
from IPython.display import display
from PIL import Image
FP = 3
for data in test_dl:
if FP==0:
break
img_batch, label_batch = data
results = model(img_batch)
confs, preds = torch.max(results, dim=1)
_, gts = torch.max(label_batch, dim=1)
preds = preds.numpy()
confs = confs.detach().numpy()
gts = gts.numpy()
for img, p, conf, g in zip(img_batch, preds, confs, gts):
if FP <= 0:
break
x = normalize_inverted(img).numpy()
x = (x * 255).astype(np.uint8).T
x = Image.fromarray(x)
if p!=g:
display(x)
print(f"Prediction : {test_ds.classes[p]} ({conf:0.4f})")
print(f"Ground Truth : {test_ds.classes[g]}")
FP -= 1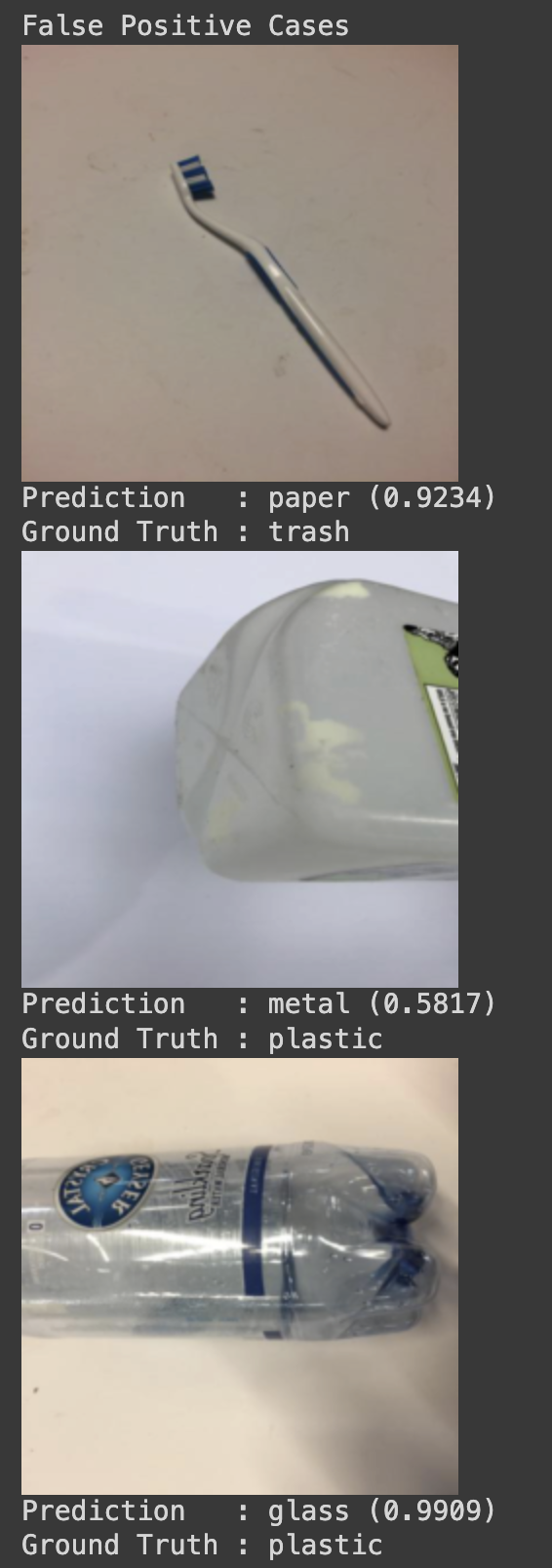
- 정답 케이스 살펴보기

'ML&DL > CV' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Object Detection] Yolo를 이용한 실내 공간의 객체 검출 (0) | 2023.11.21 |
|---|---|
| [Computer Vision] Object Detection (객체 검출) (1) | 2023.11.21 |
| [Computer Vision] Classification (0) | 2023.11.21 |
| [Computer Vision] 컴퓨터 비전의 데이터 (2) | 2023.11.21 |
| [Computer Vision] CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) (2) | 2023.11.09 |